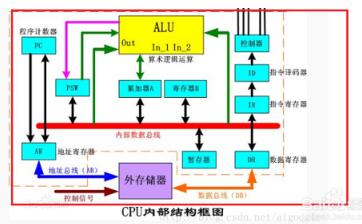
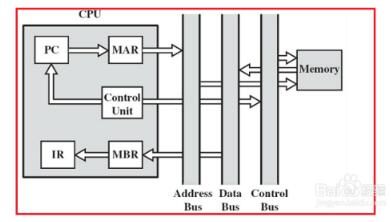
Each step of the computer can be divided into three phases. That is, the instruction-----analysis instruction-----execution instruction. The task of fetching instructions is to read the current instruction from the program memory according to the value in the program counter PC and send it to the instruction register. The task of analyzing the instruction phase is to take out the instruction opcode in the instruction register, decode it, and analyze the nature of the instruction. If the instruction requires an operand, look for the operand address. The process of the computer executing the program is actually repeating the above operation process one by one, until the stop instruction can be cycled to wait for the instruction. When a general computer is working, the program and data are first sent to the memory through the input interface circuit and the data bus through an external device, and then taken out one by one. However, the programs in the microcontroller are generally fixed in the on-chip or off-chip program memory by the writer in advance. Therefore, the instruction can be executed upon startup. CPU instruction execution flow chart Below we will give an example to illustrate the execution of the instruction: At startup, the program calculator PC becomes 0000H. Then the microcontroller automatically enters the execution program process under the action of the sequential circuit. The execution process is actually a loop process of fetching instructions (taking out the stage of instructions stored in memory beforehand) and executing instructions (analysing and executing instructions). For example, the execution instruction: MOV A, #0E0H, whose machine code is "74H E0H", the function of this instruction is to send the operand E0H to the accumulator. 74H has been stored in the 0000H unit, and E0H has been stored in the 0001H unit. When the microcontroller starts running, it first enters the fetching phase, in the order: 1. The contents of the program counter (in this case, 0000H) are sent to the address register; 2. The content of the program counter is automatically incremented by 1 (becomes 0001H); 3. The contents of the address register (0000H) are sent to the memory through the internal address bus, and the address in the memory is decoded, so that the unit with the address 0000H is selected; 4. The CPU makes the read control line valid; 5. The contents of the selected memory cell (74H at this time) are sent to the internal data bus under the control of the read command. Since it is the fetch stage, the content is sent to the instruction register via the data bus. At this point, the instruction phase is completed and enters the stage of decoding analysis and execution instructions. Since the content entered into the instruction register is 74H (opcode), after decoding by the decoder, the microcontroller knows that the instruction is to send a number to the A accumulator, and the number is the next one in the code. Storage unit. Therefore, to execute the instruction, the data (E0H) must be taken out of the memory and sent to the CPU, that is, the second byte is also taken in the memory. The process is very similar to the fetching phase, except that the PC is already 0001H. The instruction decoder, in conjunction with the timing component, generates a micro-operation series of 74H opcodes that cause the digital E0H to be fetched from the 0001H unit. Because the instruction is required to send the fetched number to the A accumulator, the fetched number enters the A accumulator via the internal data bus instead of entering the instruction register. At this point, the execution of an instruction is completed. In the single-chip microcomputer, PC=“0002Hâ€, the PC automatically adds 1 every time the CPU fetches or retrieves the memory, and the MCU enters the next fetching stage. This process is repeated until a pause command is received or the loop waits for a command pause. The CPU executes the instructions one by one, completing all the rules. 1, the first step we first look at the internal structure of the cpu, mainly including the register, controller, ALU arithmetic logic unit, the controller also contains the operation controller, counter, register, etc., as shown below: 2, the second step, after we understand the internal structure of the cpu, it is easier to understand how the cpu executes the instruction. The cpu execution instruction is mainly divided into five stages, from the instruction fetch, the instruction decoding, the execution instruction, and the access to the main Save, and finally write back the results, the specific cpu execution process is shown below: 3, the third step we first look at the first and second stages of the cpu execution instruction, how does the cpu fetch the instruction and decode the instruction, first fetch the instruction from the main memory, then put it into the register, and finally decode the instruction, so The first and second stages of completing the cpu execution instruction are as follows: 4. The fourth step cpu executes the third and fourth stages of the instruction. First, according to the operation specified by the instruction, the specific function is completed. Finally, the main memory, the operand, and the physical address are obtained, and the execution instruction and the access to the main memory are completed. Stage, as shown below: 5, the fifth step in the fourth phase of the cpu access to the main memory, you need to get the physical address, the specific read and write process is shown below: 6, the sixth step we can also look at how the cpu is reading instructions, the following is the working principle of cpu, as shown below: 7. The seventh step cpu execution instruction goes to the fifth stage, and the last stage returns the result, and writes the running result data of the third stage execution instruction to a storage form, and the cpu successfully executes one instruction. As shown below High Frequency Inverter Charger High Frequency Inverter Charger,High Frequency Inverter Transformers,Inverter Charger,High Frequency Car Power Charger SUZHOU DEVELPOWER ENERGY EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.fisoph-power.com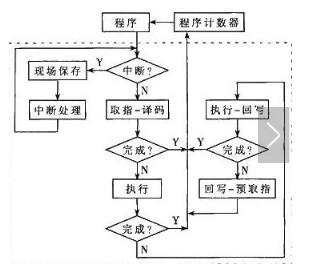


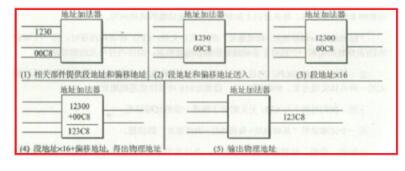
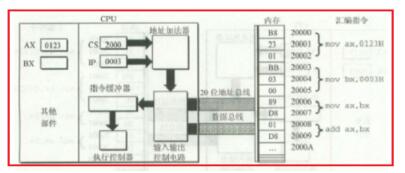

Detailed process of cpu execution instructions
Detailed process of cpu execution instructions